ROTATIONAL MISMATCH OF SELF-ALIGN TIBIAL COMPONENT IN POSTERIOR-STABILIZED (PS) TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55374/jseamed.v1i2.25Keywords:
Rotational, TKA, self align, tibial componentAbstract
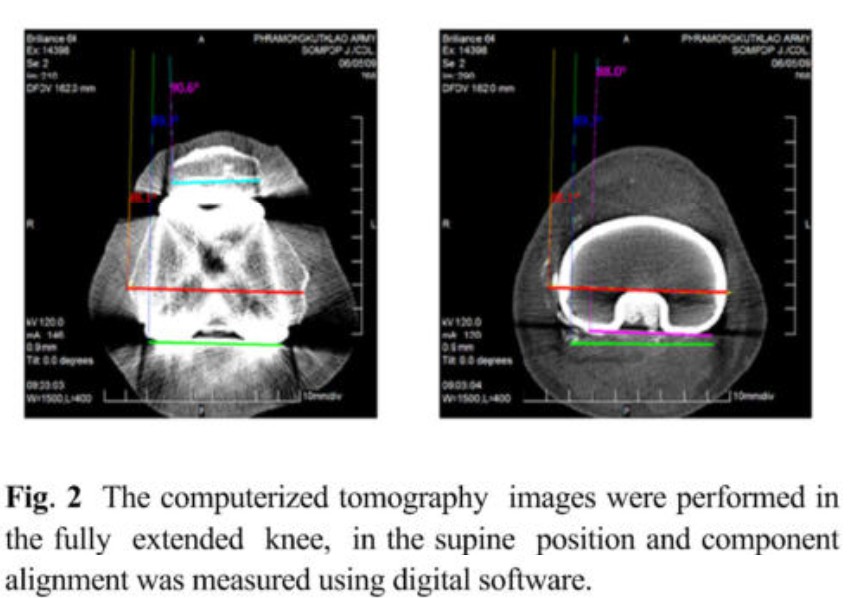
Background: Rotational alignment of femoral and tibial prosthesis is one of the important factors for outcomes of total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Rotational malalignment may lead to patellar maltracking, anterior knee pain, femoro-tibial flexion instability and premature wear of the polyethylene inlay. Several studies have demonstrated higher revision rates and less favorable clinical results among patients with rotational malalignment. The transepicondylar axis is widely accepted as the best representation of the functional flexion-extension axis of the knee. On the other hand, no comparable agreement exists for tibial rotational alignment Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine the accurate rotational alignment of components by posterior cruciate lignment substituting TKA using the center-post self-align technique. Method: From January 2007 to May 2009, 54 patients (60 knees) underwent the cemented, posterior ligament substituting TKA using the center-post self-align technique of the tibial component and performed computer tomography postoperatively. The rotational angle between the femoral and tibial components and the rotational variance from the transepicondylar axis were measured. Results: The rotational alignment of femoral components were 90% in the neutral group: 48.3% external rotate (mean 1.15 , range 0.1 – 4.9), 48.3% internal rotate (mean 1.53 , range 0.2 -3.8) and 3.4% were in neutral alignment. The rotation alignment of tibial components were 71.7% in the neutral group: 41.2% external rotate (mean 2.03 , range 0.2 -6.7), 56.7% internal rotate (mean 2.59 , range 0.3 -6.7) and 1.67% had neutral alignment. We found no rotational mismatch between femoral and tibial components in this study. All 60 knees had good patellar tracking by no thumb test technique without lateral released procedure. Conclusion: Femoral component rotations were mostly in the safe zone. Using the center-post self-align technique in posterior cruciate ligament substiting TKA, tibial component rotation was much more varied than the femur. However, all tibial component rotations were in between medial most and medial 1/3 of the tibial tuberble
Downloads
Metrics
References
Asano T, Akagi M, Nakamura T: The functional flexion-extension axis of the knee corresponds to the surgical epicondylar axis: in vivo analysis using a biplanar image-matching technique. J Arthroplasty 20(8):1060, 2005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2004.08.005
Churchill DL, Incavo SJ, Johnson CC, Beynnon BD: The transepicondylar axis
approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res(356):111, 1998
Miller MC, Berger RA, Petrella AJ, Karmas A, Rubash HE: Optimizing femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop(392):38, 2001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200111000-00005
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C: Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res(436):172, 2005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000160027.52481.32
Olcott CW, Scott RD: The Ranawat Award. Femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res(367):39, 1999 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199910000-00005
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L: Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res(392):46, 2001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200111000-00006
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE: Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop(356):144, 1998 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199811000-00021
Hofmann S, Romero J, Roth-Schiffl E, Albrecht T: [Rotational malalignment of the components may cause chronic pain or early failure in total knee arthroplasty]. Orthopade 32(6):469, 2003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00132-003-0503-5
Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, Math K, Dennis DA, Anderson DT: Correlation between condylar lift-off and femoral component alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res(403):143, 2002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200210000-00022
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG: Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res(299):31, 1994 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199402000-00005
Romero J, Stahelin T, Binkert C, Pfirrmann C, Hodler J, Kessler O: The clinical consequences of flexion gap asymmetry in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22(2):235, 2007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2006.04.024
Incavo SJ, Wild JJ, Coughlin KM, Beynnon BD: Early Revision for Component Malrotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:131-6, 2007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/BLO.0b013e3180332d97
Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Goetz DD, et al. Tibialpost impingement in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002:83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200211000-00014
Banks SA, Harman MK, Hodge WA. Mechanism of anterior impingement damage in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg—American Volume 2002; 84-A(Suppl 2):37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200200002-00004
Puloski SK, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, et al. Tibial post wear in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty.An unrecognized source of polyethylene debris. J Bone Joint Surg—American Volume 2001;83-A:390. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200103000-00011
Olcott CW, Scott RD: A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15(1):22, 2000 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-5403(00)91051-9
Chowdhury EA, Porter ML, et al: How is the tibial tray aligned to the femoral prosthesis in a total knee arthroplasty?: a survey of opinion from BASK? Knee 2005;12:79-80.
Churchill DL, Incavo SJ, Johnson CC, et al: The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop 1998;356:111–118 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199811000-00016
Heesterbeek PJC, Beumers MPC, Jacobs WCH, Havinga ME, Wymenga AB. A comparison of reproducibility of measurement techniques for patellar position on axial radiograph after total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2007;14;411-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2007.06.006
Kessler O, Lacatusu E, Sommers MB, Mayr E, Bottlang M: Malrotation in total knee arthroplasty: Effect on tibial cortex strain captured by laser-based strain acquisition. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 21(6):603-9, 2006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2006.01.011
Uehara K, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, et al: Bone anatomy and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 2002;402:196-201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200209000-00018
Chowdhury EA, Porter ML, et al: How is the tibial tray aligned to the femoral prosthesis in a total knee arthroplasty?: a survey of opinion from BASK? Knee 2005;12:79-80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2004.05.007
Eckhoff DG, Metzger RG, Vandewalle MV: Malrotation associated with implant alignment technique in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 1995;321:28-31 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199512000-00005
Nagamine R, Miyaanishi K, Miura H, et al: Medial torsion of the tibia in Japanese patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Orthop 2003;408:218. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200303000-00028
Sun T, Lu H, Hong N, et al:Bony Landmarks and Rotational Alignment in TotalKnee Arthroplasty for Chinese Osteoarthritic Knees With Varus or Valgus Deformities.The Journal of Arthroplasty 2009;24:3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.021
Klein, R. MS; Serpe, L. MS; Kester, M. A. PhD; Edidin, A. PhD; Fishkin, Z. PhD; Mahoney, O. M. MD; Schmalzried, T. P. MD. Rotational Constraint in Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research: May 2003 - Volume 410 - Issue - pp 82-89 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000063596.67412.a0
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The Journal of Southeast Asian Medical Research will hold the copyright to all published articles. The publisher's production department handles copyright forms once a manuscript is accepted and scheduled for publication.







