DOES THE PLATELET CONCENTRATION IN PLATELET RICH PLASMA INFLUENCE THE OUTCOMES OF PRIMARY KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55374/jseamed.v5i1.80Keywords:
Concentration of platelets, Platelet rich plasma, Primary knee OAAbstract
Background: Growth factors in platelets have been extensively studied and were reported to be used to stimulate cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis (OA).
Objective: This study aimed to observe the influence of platelet concentration in platelet rich plasma (PRP) on the outcomes of primary knee OA.
Methods: Eighty-nine patients undergoing PRP injection in unilateral primary knee OA were assessed using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) questionnaire and visual analog scale (VAS) before intervention at 3 weeks, 3 months, 6 months and 12 months after treatment. A small aliquot of PRP was sent for bacteriologic examination and evaluation of the platelet count. A student t-test was conducted to compare WOMAC and VAS score among patients before PRP injection (baseline) and at each follow-up. The platelet count and their influence on outcomes were also analyzed using Pearson`s correlation coefficient.
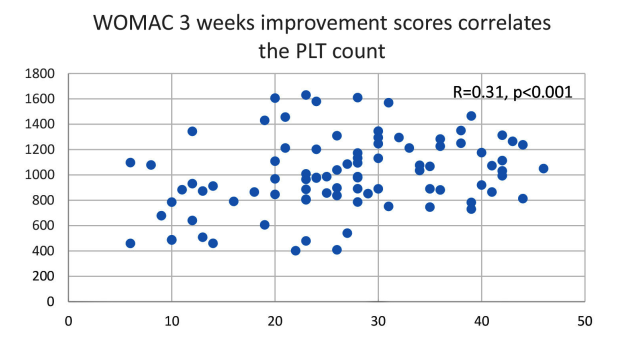
Results: Statistically significant differences were observed in the WOMAC score between baseline (M=47.08, SD=8.50) and 3 weeks (M=20.37, SD= 10.09, p< 0.001), 3 months (M= 23.24, SD= 11.39, p<0.001), 6 months (M= 29.89, SD=14.95, p <0.001), and final follow-up at 12 months (M= 27.78, SD= 16.56, p<0.001). Also a significant difference was observed in VAS between baseline (M=69.02, SD= 9.58) and 3 weeks (M= 36.23, SD= 15.72, p <0.001), 3 months (M= 37.04, SD= 17.30, p <0.001), 6 months (M= 42.58, SD=22.15, p <0.001) and 12 months (M=39.15, SD= 23.96, p <0.001). The mean platelet count in PRP injection was 1000.66x103platelets/mL (402x103platelets/ml to 1630x103platelets/mL). Positive correlations were discovered between the concentration of the platelet and the mean improvement WOMAC scores and VAS at 3 weeks (r =0.31, r=0.40), 3 months (r=0.10, r=0.23), 6 months (r=0.08, r=0.30) and 12 months after intervention (r=0.12, r=0.23), respectively.
Conclusion: Higher concentrations of platelets in the PRP had a better effect on outcomes of primary knee OA especially at three weeks after injection.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Laudy AB, Bakker EW, Rekers M, Moen MH. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections in osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and meta- analysis. Br J Sports Med 2015; 49: 657–72. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2014-094036
Anitua E, Sanchez M, Javier Aguirre JJ, Prado R, Padilla S, Orive G. Efficacy and safety of plasma rich in growth factors intra-articular infiltrations in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 2014; 30: 1006–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2014.05.021
Shen L, Yuan T, Chen S, Xie X, Zhang C. The temporal effect of platelet-rich plasma on pain and physical function in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta- analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res 2017; 12: 16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-017-0521-3
Meheux CJ, McCulloch PC, Lintner DM, Varner KE, Harris JD. Efficacy of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injections in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Arthroscopy 2016; 32: 495–505. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2015.08.005
Chang KV, Hung CY, Aliwarga F, Wang TG, Han DS, Chen WS. Comparative effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating knee joint cartilage degenerative pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2014; 95: 562–75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2013.11.006
Patel S, Dhillon M. S, Aggarwal S, Marwaha N, Jain A. Treatment of platelet rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41: 356-64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546512471299
Kon E, Buda R, Filardo G, Martino AD, Timoncini A, Cenacchi A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intraarticular knee injections produced favourable results on degenerative cartilage lesions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2010; 18: 472-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-009-0940-8
Sampson S, Gerhardt M, Mandelbaum B. Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008; 1:165-74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-008-9032-5
Nurden AT. Platelets, inflammation and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost 2011; 105 (suppl 1): S13-S33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1160/THS10-11-0720
Dhillon RS, Schwarz EM, Maloney MD. Platelet-rich plasma therapy-future or trend? Arthritis Res Ther 2012; 14: 219. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3914
Hickey DG, Frenkel SR, Di Cesare PE. Clinical applications of growth factors for articular cartilage repair. Am J Orthop 2003; 32: 70-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ABME.0000007788.41804.0d
Dhurat R, Sukesh M. Principles and methods of preparation of platelet- rich plasma: A review and author’s perspective. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2014; 7: 189-97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.150734
Spakova T, Rosocha J, Lacko M, Harvanova D, Gharaibeh A. Treatment of knee joint osteoarthritis with autologous platelet rich plasma in comparison with hyaluronic acid. Am J Phys Med Rehabi 2012; 91: 1-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0b013e31824aab72
Magalon J, Bausset O, Serratrice N, Giraudo L, Aboudou H, Veran J, et al. Characterization and comparison of 5 platelet- rich plasma preparations in a single-donor model. Arthroscopy 2014; 30: 629–38.
Sundman EA, Cole BJ, Fortier LA. Growth factor and catabolic cytokine concentrations are influenced by the cellular composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med 2011; 39: 2135–140.
Magalon J, Bausset O, Serratrice N, Giraudo L, Adoudou H, Veran J, et al. Characterization and comparison of 5 platelet- rich plasma preparations in a single-donor model. Arthroscopy 2014; 30: 629–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2014.02.020
Sundman EA, Cole BJ, Fortier LA. Growth factor and catabolic cytokine concentrations are influenced by the cellular composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med 2011; 39: 2135–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546511417792
Castillo TN, Pouliot MA, Kim HJ, Dragoo JL. Comparison of growth factor and platelet concentration from commercial platelet- rich plasma separation systems. Am J Sports Med 2011; 39: 266. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546510387517
Eppley BL, Woodell JE, Higgins J. Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: implications for wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004; 114: 1502-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000138251.07040.51
Weibrich G, Hansen T, Kleis W, Buch R, Hitzler WE. Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 2004; 34: 665-71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2003.12.010
Dernek B, Kesiktas FM, Duymus TM, Aydin T, Isiksacan N, Diracoglu D, et al. Effect of platelet concentration on clinical improvement in treatment of early stage- knee osteoarthritis with platelet-rich plasma concentrations. J Phys Ther Sci 2017; 29: 896-901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.29.896
Aqil A, Jacobs L. Physical therapy or platelet rich plasma injections in the treatment of tennis elbow: A ramdomised clinical trial. Webmed Central ORTHOPAEDICS 2010; 1: WMC00701
Engebretsen L, Schamasch P. The use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine- The international olympic committee opinion. Operat Tech Orthop 2012; 22: 43-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.oto.2011.10.006
Filardo G, Kon E, Buda R, Timoncini A, Martino AD, Cenacchi A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra articular knee injections for the treatment of degenerative cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2011; 19: 528-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1238-6
Andia I, Sanchez M, Maffulli N. Joint pathology & platelet rich plasma therapies. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2012; 12: 7-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2012.632765
Sánchez M, Fiz N, Azofra J, Usabiaga J, Recalde EA, Gutierrez AG, et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF Endoret) versus hyaluronic acid in the ahort-term treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 2012; 28: 1070-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2012.05.011
Chatterjee A, Debnath K. Comparative evaluation of growth factors from platelet concentrates: An in vitro study. J Indian Soc Periodontol 2019; 23: 322-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/jisp.jisp_678_18
Gato-Calvo L, Magalhaes J, Ruiz- Romero C, Blanco FJ, Burguera EF. Platelet- rich plasma in osteoarthritis treatment: review of current evidence. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2019; 10: 1-18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622319825567
Machado ES, Leite R, Santos CCd. Artuso GL, Gluszczak F, Jesus LGD, et.al. Turn down-turn up: a simple and low- cost protocol for preparing platelet-rich plasma. CLINICS 2019; 74: e1132 DOI: https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2019/e1132
Everts PAM, Mahoney CB Hoffmann JJML, Schönberger JPAM, Box HAM, Zundert AV, et al. Platelet-rich plasma preparation using three devices: implications for platelet activation and platelet growth factor release. Growth Factors 2006; 24: 165-71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08977190600821327
Kevy SV, Jacobson MS. Comparison of methods for point of care preparation of autologous platelet gel. J Extra Corpor Technol 2004; 36: 28-35.
Tamimi FM, Montalvo S, Tresguerres I, Blanco Jerez L. A comparative study of 2 methods for obtaining platelet-rich plasma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007; 65:1084-93. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2006.09.012
Kuffler DP. Variables affecting the potential efficacy of PRP in providing chronic pain relief. J Pain Res 2019; 12: 109-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S190065
Bielecka AC, Ehrenfest DMD, Lubkowska A, Bielecki T. Microbicidal properties of leukocyte-and platelet-rich plasma/fibrin(L-PRP/L-PRF): New perspectives. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2012; 26 (2 Suppl 1): 43S-52S.
Lana JF, Macedo A, Ingrao ILG, Huber SC, Santos GS, Santana MHA. Leukocyte-rich PRP for knee osteoarthritis: Current concepts. J Clin Orthop Trauma 2019: 10 (Suppl 1): S179-S82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2019.01.011
Milants C, Bruyere O, Kaux JF. Responders to platelet-rich plasma in osteoarthritis: A technical analysis. Biomed Res Int 2017: 7538604. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7538604
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The Journal of Southeast Asian Medical Research will hold the copyright to all published articles. The publisher's production department handles copyright forms once a manuscript is accepted and scheduled for publication.







